Note
Click here to download the full example code
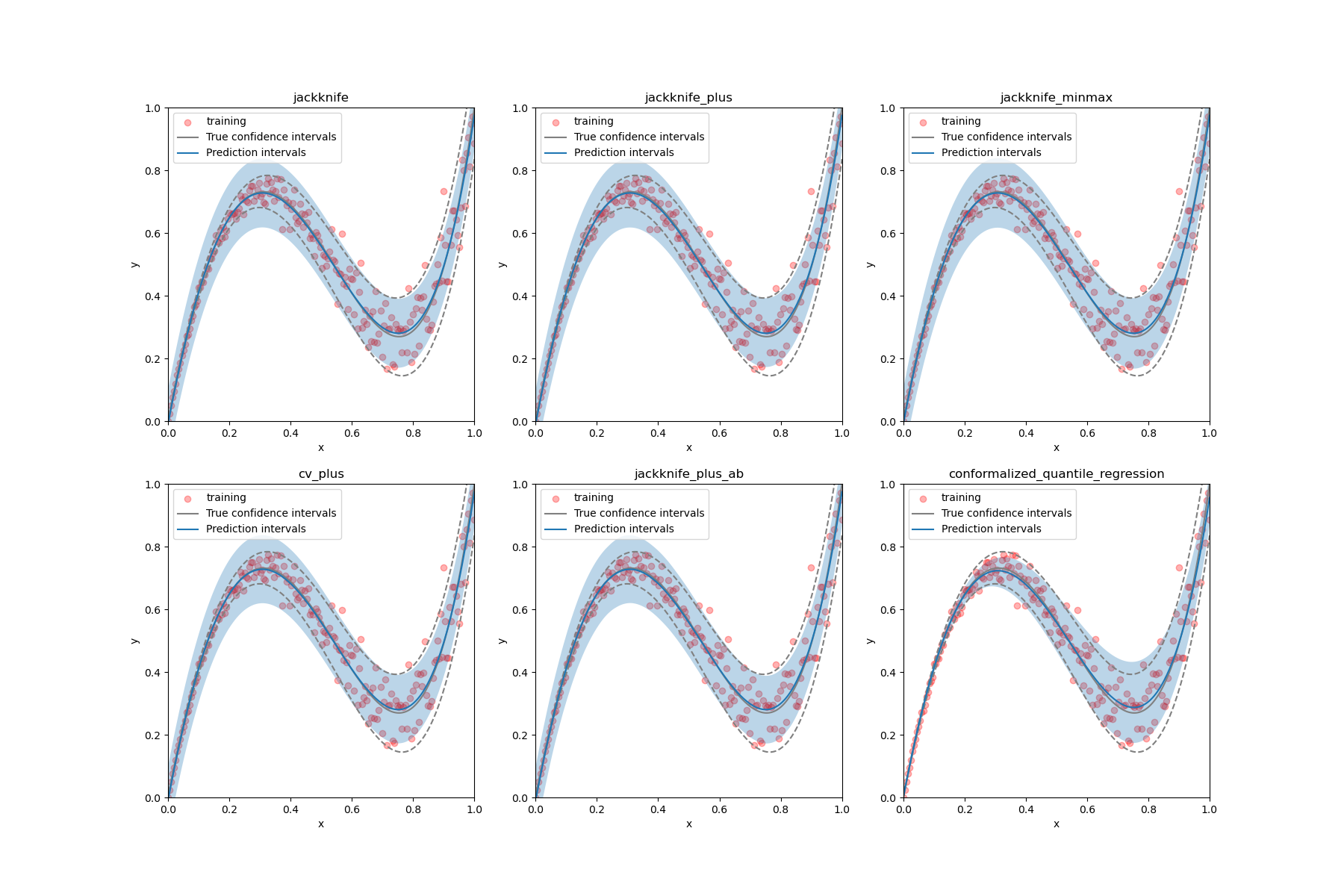
Estimate the prediction intervals of 1D heteroscedastic data¶
MapieRegressor and
MapieQuantileRegressor is used
to estimate the prediction intervals of 1D heteroscedastic data using
different strategies. The latter class should provide the same
coverage for a lower width of intervals because it adapts the prediction
intervals to the local heteroscedastic noise.
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as np
import scipy
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, QuantileRegressor
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from mapie._typing import NDArray
from mapie.regression import MapieQuantileRegressor, MapieRegressor
from mapie.subsample import Subsample
random_state = 42
def f(x: NDArray) -> NDArray:
"""Polynomial function used to generate one-dimensional data"""
return np.array(5 * x + 5 * x ** 4 - 9 * x ** 2)
def get_heteroscedastic_data(
n_train: int = 200, n_true: int = 200, sigma: float = 0.1
) -> Tuple[NDArray, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray]:
"""
Generate one-dimensional data from a given function,
number of training and test samples and a given standard
deviation increases linearly with x.
The training data data is generated from an exponential distribution.
Parameters
----------
n_train : int, optional
Number of training samples, by default 200.
n_true : int, optional
Number of test samples, by default 1000.
sigma : float, optional
Standard deviation of noise, by default 0.1
Returns
-------
Tuple[NDArray, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray]
Generated training and test data.
[0]: X_train
[1]: y_train
[2]: X_true
[3]: y_true
[4]: y_true_sigma
"""
np.random.seed(random_state)
q95 = scipy.stats.norm.ppf(0.95)
X_train = np.linspace(0, 1, n_train)
X_true = np.linspace(0, 1, n_true)
y_train = f(X_train) + np.random.normal(0, sigma, n_train) * X_train
y_true = f(X_true)
y_true_sigma = q95 * sigma * X_true
return X_train, y_train, X_true, y_true, y_true_sigma
def plot_1d_data(
X_train: NDArray,
y_train: NDArray,
X_test: NDArray,
y_test: NDArray,
y_test_sigma: NDArray,
y_pred: NDArray,
y_pred_low: NDArray,
y_pred_up: NDArray,
ax: plt.Axes,
title: str,
) -> None:
"""
Generate a figure showing the training data and estimated
prediction intervals on test data.
Parameters
----------
X_train : NDArray
Training data.
y_train : NDArray
Training labels.
X_test : NDArray
Test data.
y_test : NDArray
True function values on test data.
y_test_sigma : float
True standard deviation.
y_pred : NDArray
Predictions on test data.
y_pred_low : NDArray
Predicted lower bounds on test data.
y_pred_up : NDArray
Predicted upper bounds on test data.
ax : plt.Axes
Axis to plot.
title : str
Title of the figure.
"""
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_xlim([0, 1])
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
ax.scatter(X_train, y_train, color="red", alpha=0.3, label="training")
ax.plot(X_test, y_test, color="gray", label="True confidence intervals")
ax.plot(X_test, y_test - y_test_sigma, color="gray", ls="--")
ax.plot(X_test, y_test + y_test_sigma, color="gray", ls="--")
ax.plot(X_test, y_pred, label="Prediction intervals")
ax.fill_between(X_test, y_pred_low, y_pred_up, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_title(title)
ax.legend()
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, y_test_sigma = get_heteroscedastic_data()
polyn_model = Pipeline(
[
("poly", PolynomialFeatures(degree=4)),
("linear", LinearRegression()),
]
)
polyn_model_quant = Pipeline(
[
("poly", PolynomialFeatures(degree=4)),
("linear", QuantileRegressor(
solver="highs-ds",
alpha=0,
)),
]
)
STRATEGIES = {
"jackknife": {"method": "base", "cv": -1},
"jackknife_plus": {"method": "plus", "cv": -1},
"jackknife_minmax": {"method": "minmax", "cv": -1},
"cv_plus": {"method": "plus", "cv": 10},
"jackknife_plus_ab": {"method": "plus", "cv": Subsample(n_resamplings=50)},
"conformalized_quantile_regression": {"method": "quantile", "cv": "split"},
}
fig, ((ax1, ax2, ax3), (ax4, ax5, ax6)) = plt.subplots(
2, 3, figsize=(3 * 6, 12)
)
axs = [ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4, ax5, ax6]
for i, (strategy, params) in enumerate(STRATEGIES.items()):
if strategy == "conformalized_quantile_regression":
mapie = MapieQuantileRegressor( # type: ignore
polyn_model_quant,
**params
)
mapie.fit(X_train.reshape(-1, 1), y_train, random_state=random_state)
y_pred, y_pis = mapie.predict(X_test.reshape(-1, 1))
else:
mapie = MapieRegressor( # type: ignore
polyn_model,
agg_function="median",
n_jobs=-1,
**params
)
mapie.fit(X_train.reshape(-1, 1), y_train)
y_pred, y_pis = mapie.predict(
X_test.reshape(-1, 1),
alpha=0.05,
)
plot_1d_data(
X_train,
y_train,
X_test,
y_test,
y_test_sigma,
y_pred,
y_pis[:, 0, 0],
y_pis[:, 1, 0],
axs[i],
strategy,
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.698 seconds)