Note
Click here to download the full example code
Estimating aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties¶
This example uses MapieRegressor and
MapieQuantileRegressor to estimate
prediction intervals capturing both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties
on a one-dimensional dataset with homoscedastic noise and normal sampling.
from typing import Any, Callable, Tuple, TypeVar
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, QuantileRegressor
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from mapie._typing import NDArray
from mapie.regression import MapieQuantileRegressor, MapieRegressor
from mapie.subsample import Subsample
F = TypeVar("F", bound=Callable[..., Any])
random_state = 42
# Functions for generating our dataset
def x_sinx(x: NDArray) -> NDArray:
"""One-dimensional x*sin(x) function."""
return x * np.sin(x)
def get_1d_data_with_normal_distrib(
funct: F, mu: float, sigma: float, n_samples: int, noise: float
) -> Tuple[NDArray, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray]:
"""
Generate noisy 1D data with normal distribution from given function
and noise standard deviation.
Parameters
----------
funct : F
Base function used to generate the dataset.
mu : float
Mean of normal training distribution.
sigma : float
Standard deviation of normal training distribution.
n_samples : int
Number of training samples.
noise : float
Standard deviation of noise.
Returns
-------
Tuple[NDArray, AnNDArrayy, NDArray, NDArray, NDArray]
Generated training and test data.
[0]: X_train
[1]: y_train
[2]: X_test
[3]: y_test
[4]: y_mesh
"""
np.random.seed(random_state)
X_train = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, n_samples)
X_test = np.arange(mu - 4 * sigma, mu + 4 * sigma, sigma / 20.0)
y_train, y_mesh, y_test = funct(X_train), funct(X_test), funct(X_test)
y_train += np.random.normal(0, noise, y_train.shape[0])
y_test += np.random.normal(0, noise, y_test.shape[0])
return (
X_train.reshape(-1, 1),
y_train,
X_test.reshape(-1, 1),
y_test,
y_mesh,
)
# Data generation
mu, sigma, n_samples, noise = 0, 2.5, 300, 0.5
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, y_mesh = get_1d_data_with_normal_distrib(
x_sinx, mu, sigma, n_samples, noise
)
# Definition of our base model
degree_polyn = 10
polyn_model = Pipeline(
[
("poly", PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree_polyn)),
("linear", LinearRegression()),
]
)
polyn_model_quant = Pipeline(
[
("poly", PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree_polyn)),
("linear", QuantileRegressor(
alpha=0,
solver="highs", # highs-ds does not give good results
)),
]
)
# Estimating prediction intervals
STRATEGIES = {
"jackknife_plus": {"method": "plus", "cv": -1},
"cv_plus": {"method": "plus", "cv": 10},
"jackknife_plus_ab": {"method": "plus", "cv": Subsample(n_resamplings=50)},
"conformalized_quantile_regression": {"method": "quantile", "cv": "split"},
}
y_pred, y_pis = {}, {}
for strategy, params in STRATEGIES.items():
if strategy == "conformalized_quantile_regression":
mapie = MapieQuantileRegressor( # type: ignore
polyn_model_quant,
**params
)
mapie.fit(X_train, y_train, random_state=random_state)
y_pred[strategy], y_pis[strategy] = mapie.predict(X_test)
else:
mapie = MapieRegressor(polyn_model, **params) # type: ignore
mapie.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred[strategy], y_pis[strategy] = mapie.predict(X_test, alpha=0.05)
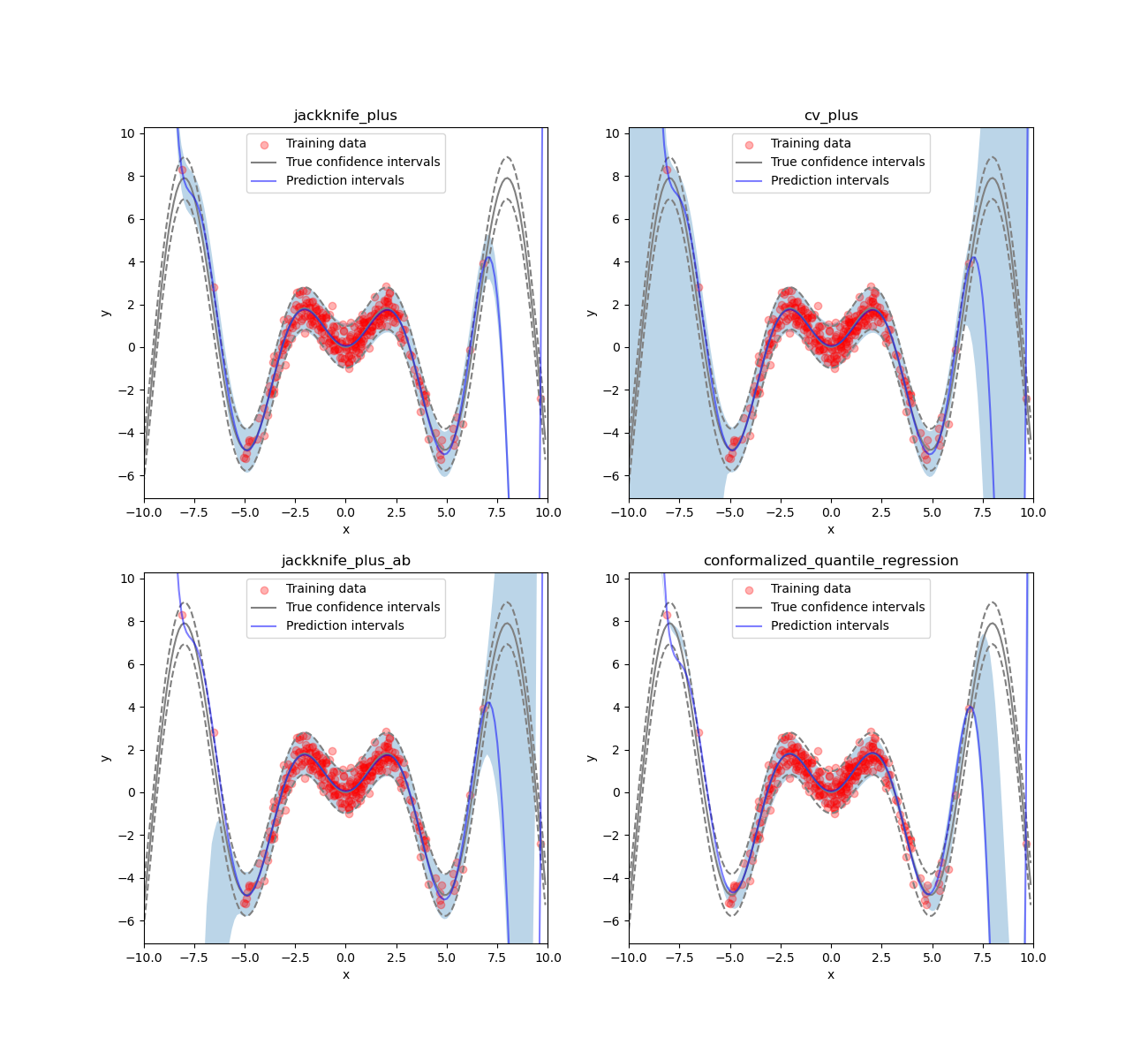
# Visualization
def plot_1d_data(
X_train: NDArray,
y_train: NDArray,
X_test: NDArray,
y_test: NDArray,
y_sigma: float,
y_pred: NDArray,
y_pred_low: NDArray,
y_pred_up: NDArray,
ax: plt.Axes,
title: str,
) -> None:
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_xlim([-10, 10])
ax.set_ylim([np.min(y_test) * 1.3, np.max(y_test) * 1.3])
ax.fill_between(X_test, y_pred_low, y_pred_up, alpha=0.3)
ax.scatter(X_train, y_train, color="red", alpha=0.3, label="Training data")
ax.plot(X_test, y_test, color="gray", label="True confidence intervals")
ax.plot(X_test, y_test - y_sigma, color="gray", ls="--")
ax.plot(X_test, y_test + y_sigma, color="gray", ls="--")
ax.plot(X_test, y_pred, color="b", alpha=0.5, label="Prediction intervals")
if title is not None:
ax.set_title(title)
ax.legend()
n_figs = len(STRATEGIES)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(13, 12))
coords = [axs[0, 0], axs[0, 1], axs[1, 0], axs[1, 1]]
for strategy, coord in zip(STRATEGIES, coords):
plot_1d_data(
X_train.ravel(),
y_train.ravel(),
X_test.ravel(),
y_mesh.ravel(),
1.96 * noise,
y_pred[strategy].ravel(),
y_pis[strategy][:, 0, 0].ravel(),
y_pis[strategy][:, 1, 0].ravel(),
ax=coord,
title=strategy,
)
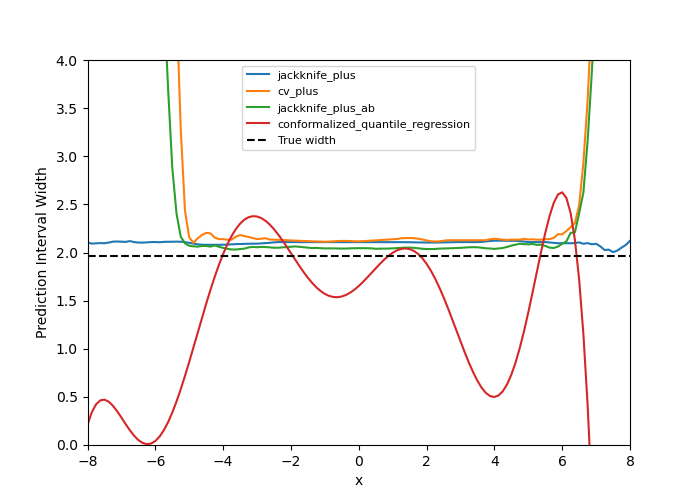
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(7, 5))
ax.set_xlim([-8, 8])
ax.set_ylim([0, 4])
for strategy in STRATEGIES:
ax.plot(X_test, y_pis[strategy][:, 1, 0] - y_pis[strategy][:, 0, 0])
ax.axhline(1.96 * 2 * noise, ls="--", color="k")
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("Prediction Interval Width")
ax.legend(list(STRATEGIES.keys()) + ["True width"], fontsize=8)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.692 seconds)