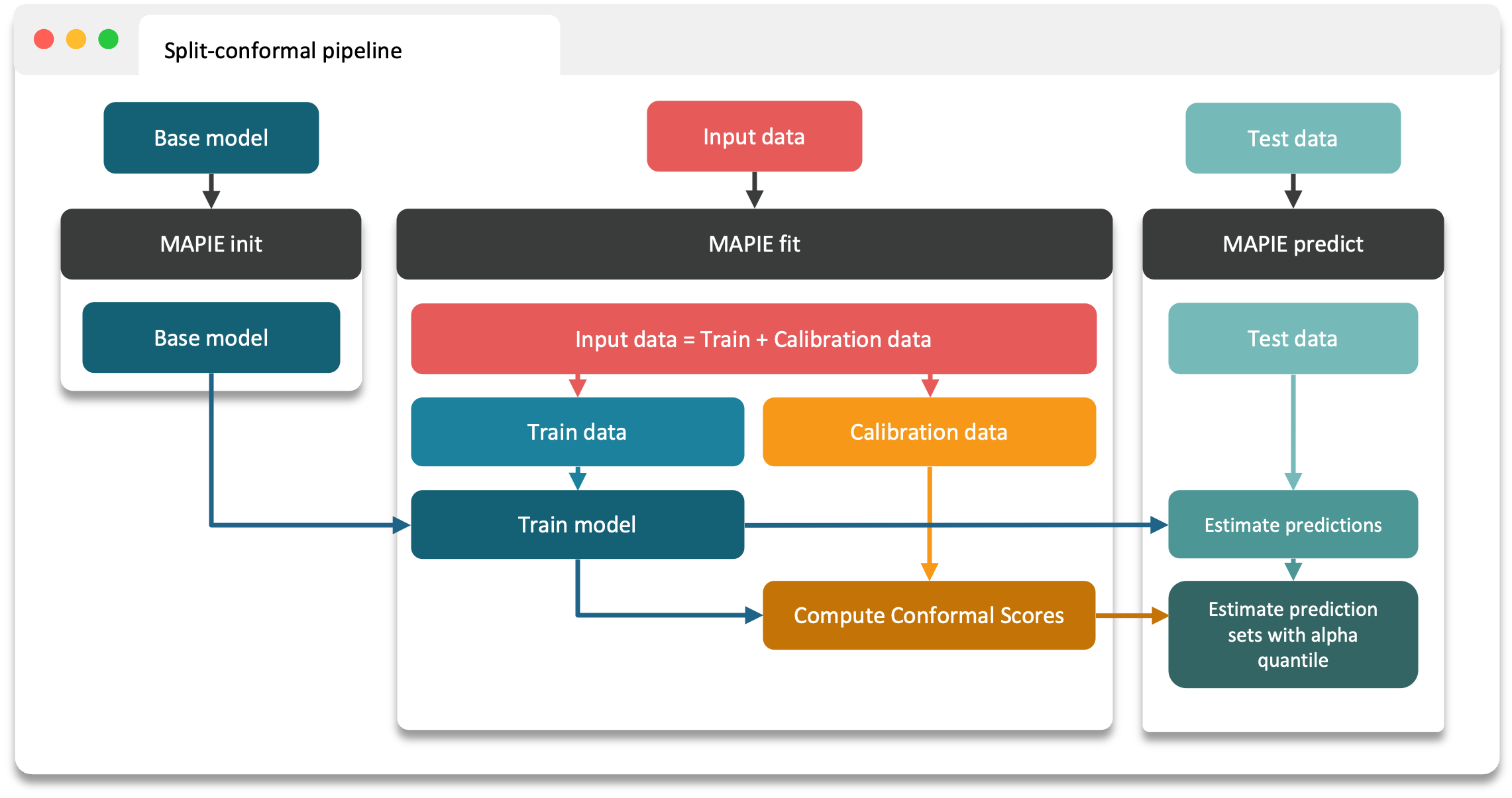
Split/Cross-Conformal Prediction¶
MAPIE is based on two types of techniques:
the split-conformal predictions,
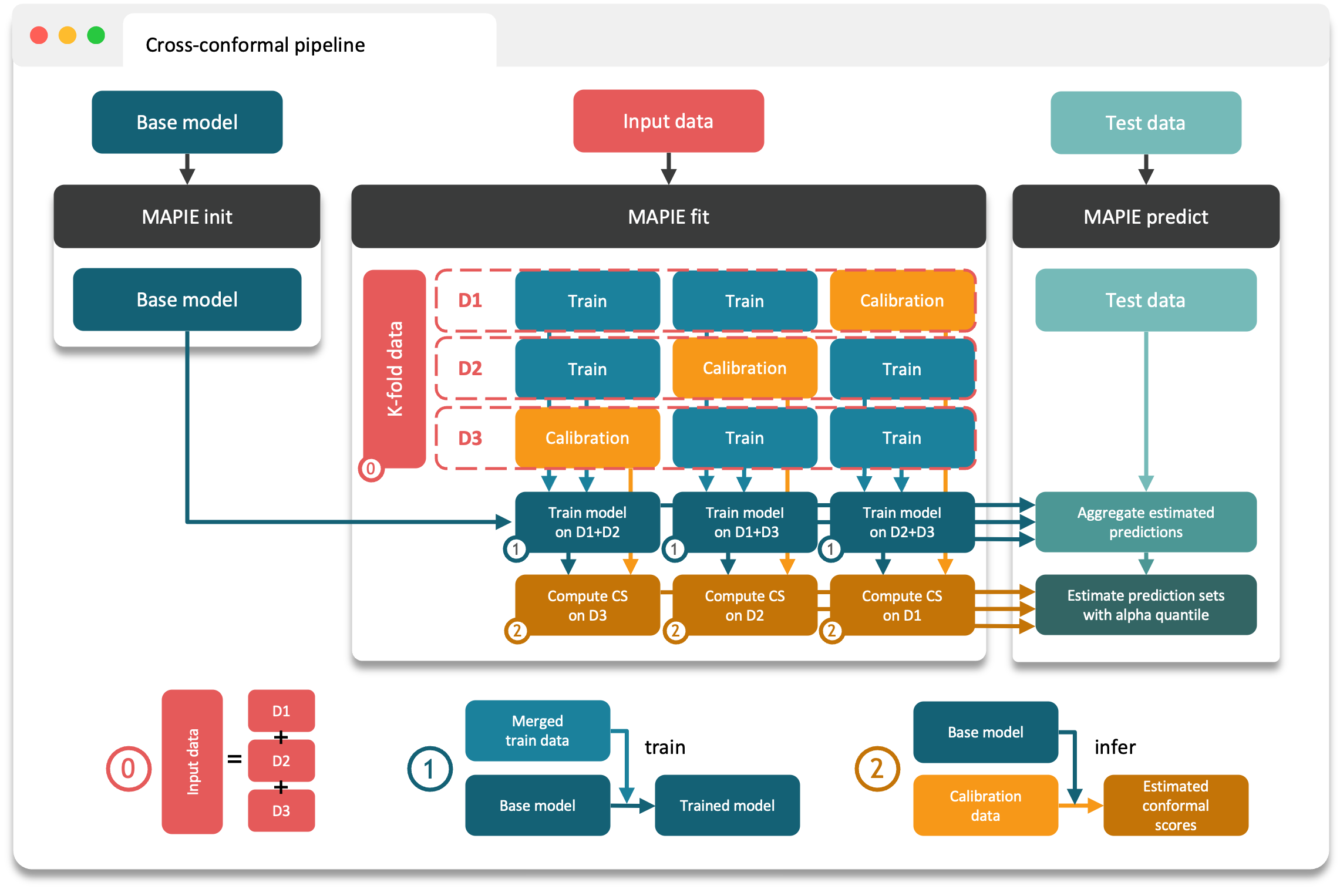
the cross-conformal predictions.
In all cases, the training/calibration process can be broken down as follows:
Identify a basic model (or pre-trained model).
Wrap it with the MAPIE class.
Fit new model to calibration data (or full data if cross-validation) to estimate conformity scores.
Predict target on test data to obtain prediction intervals/sets based on conformity scores.
1. Split conformal predictions¶
Construction of a conformity score.
Calibration of the conformity score on a calibration set not seen by the model during training.
MAPIE then uses the calibrated conformity scores to estimate sets associated with the desired coverage on new data with strong theoretical guarantees.
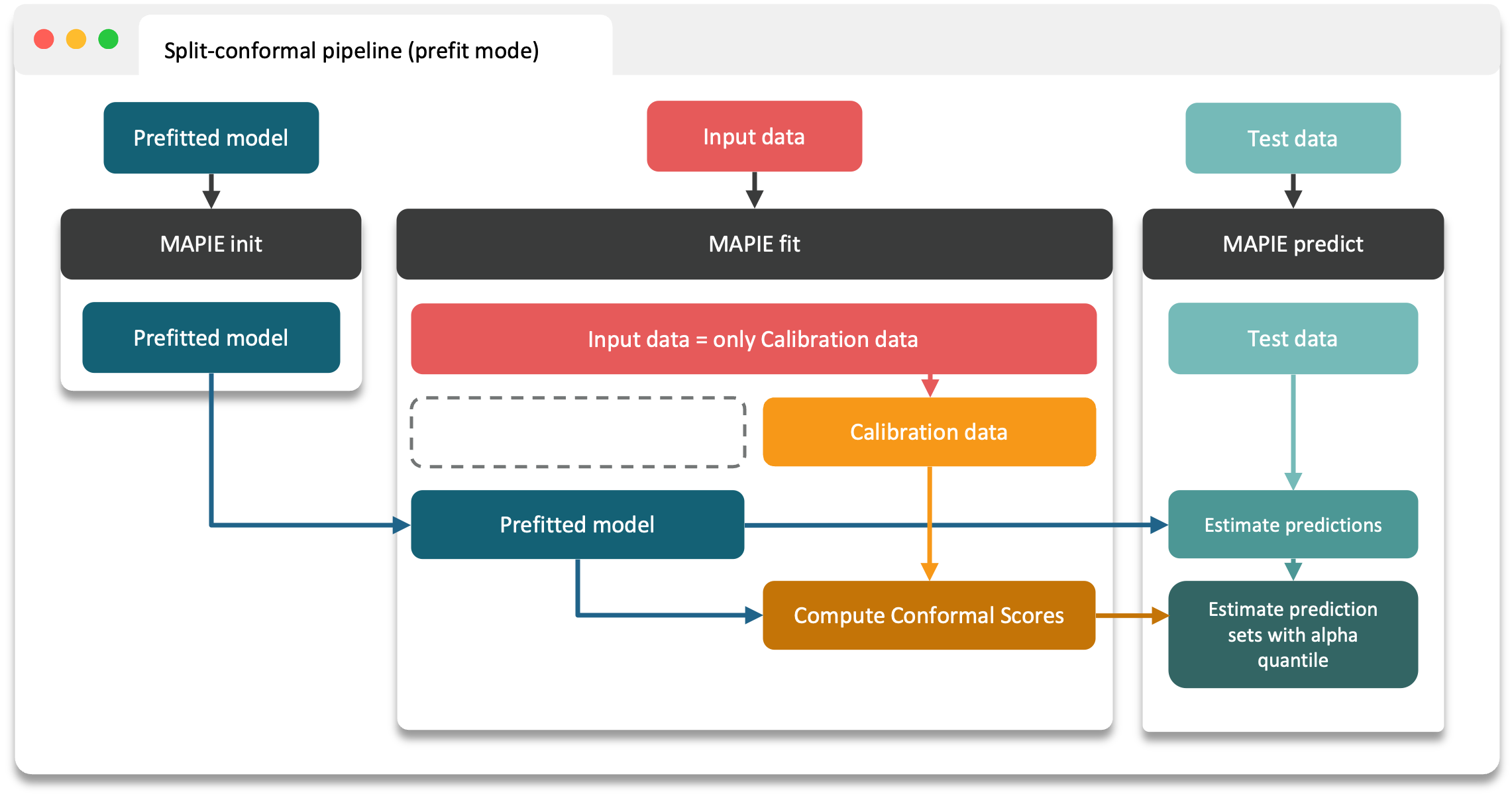
Prefit mode of split conformal predictions¶
2. Cross conformal predictions¶
Conformity scores on the whole training set obtained by cross-validation,
Perturbed models generated during the cross-validation.
MAPIE then combines all these elements in a way that provides prediction intervals on new data with strong theoretical guarantees.