Note
Click here to download the full example code
Tutorial for residual normalised score¶
We will use the sklearn california housing dataset to understand how the residual normalised score works and show the multiple ways of using it.
We will explicit the experimental setup below.
import warnings
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.ticker import FormatStrFormatter
from numpy.typing import ArrayLike
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from mapie.conformity_scores import ResidualNormalisedScore
from mapie.metrics import regression_coverage_score_v2, regression_ssc_score
from mapie.regression import MapieRegressor
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
random_state = 23
rng = np.random.default_rng(random_state)
round_to = 3
1. Data¶
The target variable of this dataset is the median house value for the California districts. This dataset is composed of 8 features, including variables such as the age of the house, the median income of the neighborhood, the average number of rooms or bedrooms or even the location in latitude and longitude. In total there are around 20k observations.
data = fetch_california_housing()
X = data.data
y = data.target
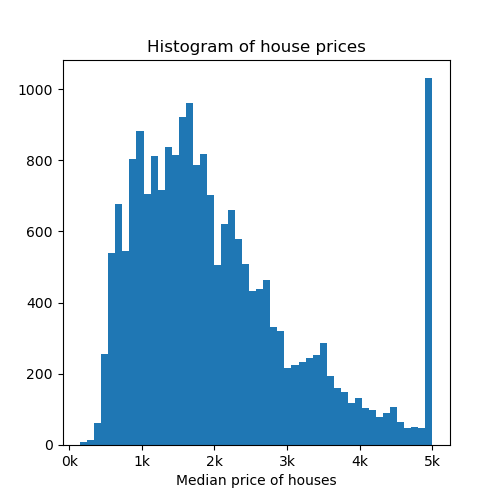
Now let’s visualize a histogram of the price of the houses.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
axs.hist(y, bins=50)
axs.set_xlabel("Median price of houses")
axs.set_title("Histogram of house prices")
axs.xaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.0f' + "k"))
plt.show()
Let’s now create the different splits for the dataset, with a training,
calibration, residual and test set. Recall that the calibration set is used
for calibrating the prediction intervals and the residual set is used to fit
the residual estimator used by the
ResidualNormalisedScore.
np.array(X)
np.array(y)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X,
y,
random_state=random_state,
test_size=0.02
)
X_train, X_calib, y_train, y_calib = train_test_split(
X_train,
y_train,
random_state=random_state
)
X_calib_prefit, X_res, y_calib_prefit, y_res = train_test_split(
X_calib,
y_calib,
random_state=random_state,
test_size=0.5
)
2. Models¶
We will now define 4 different ways of using the residual normalised score.
Remember that this score is only available in the split setup. First, the
simplest one with all the default parameters :
a LinearRegression is used for the residual
estimator. (Note that to avoid negative values it is trained with the log
of the features and the exponential of the predictions are used).
It is also possible to use it with cv="prefit" i.e. with
the base model trained beforehand. The third setup that we illustrate here
is with the residual model prefitted : we can set the estimator in parameters
of the class, not forgetting to specify prefit="True". Finally, as an
example of the exotic parameterisation we can do : we use as a residual
estimator a LinearRegression wrapped to avoid
negative values like it is done by default in the class.
class PosEstim(LinearRegression):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def fit(self, X, y):
super().fit(
X, np.log(np.maximum(y, np.full(y.shape, np.float64(1e-8))))
)
return self
def predict(self, X):
y_pred = super().predict(X)
return np.exp(y_pred)
base_model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=10, random_state=random_state)
base_model = base_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
residual_estimator = RandomForestRegressor(
n_estimators=20,
max_leaf_nodes=70,
min_samples_leaf=7,
random_state=random_state
)
residual_estimator = residual_estimator.fit(
X_res, np.abs(np.subtract(y_res, base_model.predict(X_res)))
)
wrapped_residual_estimator = PosEstim().fit(
X_res, np.abs(np.subtract(y_res, base_model.predict(X_res)))
)
# Estimating prediction intervals
STRATEGIES = {
"Default": {
"cv": "split",
"conformity_score": ResidualNormalisedScore()
},
"Base model prefit": {
"cv": "prefit",
"estimator": base_model,
"conformity_score": ResidualNormalisedScore(
split_size=0.5, random_state=random_state
)
},
"Base and residual model prefit": {
"cv": "prefit",
"estimator": base_model,
"conformity_score": ResidualNormalisedScore(
residual_estimator=residual_estimator,
random_state=random_state,
prefit=True
)
},
"Wrapped residual model": {
"cv": "prefit",
"estimator": base_model,
"conformity_score": ResidualNormalisedScore(
residual_estimator=wrapped_residual_estimator,
random_state=random_state,
prefit=True
)
},
}
y_pred, intervals, coverage, cond_coverage = {}, {}, {}, {}
num_bins = 10
alpha = 0.1
for strategy, params in STRATEGIES.items():
mapie = MapieRegressor(**params, random_state=random_state)
if mapie.conformity_score.prefit:
mapie.fit(X_calib_prefit, y_calib_prefit)
else:
mapie.fit(X_calib, y_calib)
y_pred[strategy], intervals[strategy] = mapie.predict(X_test, alpha=alpha)
coverage[strategy] = regression_coverage_score_v2(
y_test, intervals[strategy]
)
cond_coverage[strategy] = regression_ssc_score(
y_test, intervals[strategy], num_bins=num_bins
)
def yerr(y_pred, intervals) -> ArrayLike:
"""
Returns the error bars with the point prediction and its interval
Parameters
----------
y_pred: ArrayLike
Point predictions.
intervals: ArrayLike
Predictions intervals.
Returns
-------
ArrayLike
Error bars.
"""
return np.abs(np.concatenate(
[
np.expand_dims(y_pred, 0) - intervals[:, 0, 0].T,
intervals[:, 1, 0].T - np.expand_dims(y_pred, 0),
],
axis=0,
))
def plot_predictions(y, y_pred, intervals, coverage, cond_coverage, ax=None):
"""
Plots y_true against y_pred with the associated interval.
Parameters
----------
y: ArrayLike
Observed targets
y_pred: ArrayLike
Predictions
intervals: ArrayLike
Prediction intervals
coverage: float
Global coverage
cond_coverage: float
Maximum violation coverage
ax: matplotlib axes
An ax can be provided to include this plot in a subplot
"""
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 5))
ax.set_xlim([-0.5, 5.5])
ax.set_ylim([-0.5, 5.5])
error = y_pred - intervals[:, 0, 0]
warning1 = y_test > y_pred + error
warning2 = y_test < y_pred - error
warnings = warning1 + warning2
ax.errorbar(
y[~warnings],
y_pred[~warnings],
yerr=np.abs(error[~warnings]),
color="g",
alpha=0.2,
linestyle="None",
label="Inside prediction interval"
)
ax.errorbar(
y[warnings],
y_pred[warnings],
yerr=np.abs(error[warnings]),
color="r",
alpha=0.3,
linestyle="None",
label="Outside prediction interval"
)
ax.scatter(y, y_pred, s=3, color="black")
ax.plot([0, max(max(y), max(y_pred))], [0, max(max(y), max(y_pred))], "-r")
ax.set_title(
f"{strategy} - coverage={coverage:.0%} " +
f"- max violation={cond_coverage:.0%}"
)
ax.set_xlabel("y true")
ax.set_ylabel("y pred")
ax.legend()
ax.grid()
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(12, 10))
for ax, strategy in zip(axs.flat, STRATEGIES.keys()):
plot_predictions(
y_test,
y_pred[strategy],
intervals[strategy],
coverage[strategy][0],
cond_coverage[strategy][0],
ax=ax
)
fig.suptitle(f"Predicted values and intervals of level {alpha}")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
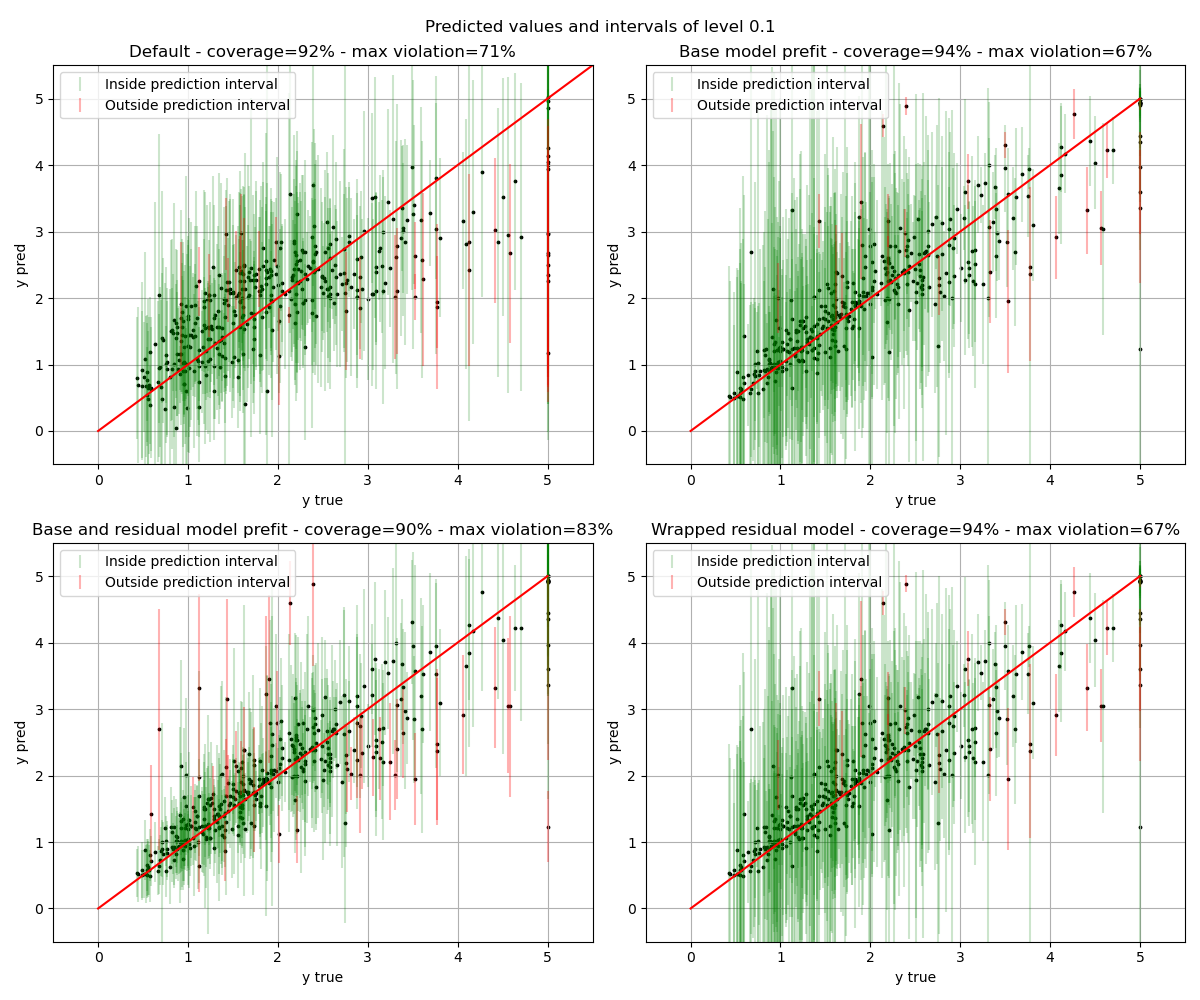
The results show that all the setups reach the global coverage guaranteed of 1-alpha. It is interesting to note that the “base model prefit” and the “wrapped residual model” give exactly the same results. And this is because they are the same models : one prefitted and one fitted directly in the class.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 3.626 seconds)